The computer is an incredibly powerful tool. It handles complex tasks efficiently saving us hours of time whether it’s performing calculations or organizing data. It allows us to connect to the internet and access knowledge from across the globe. Indeed, the computer is a remarkable gift of science.
🖥️ Types of Computers
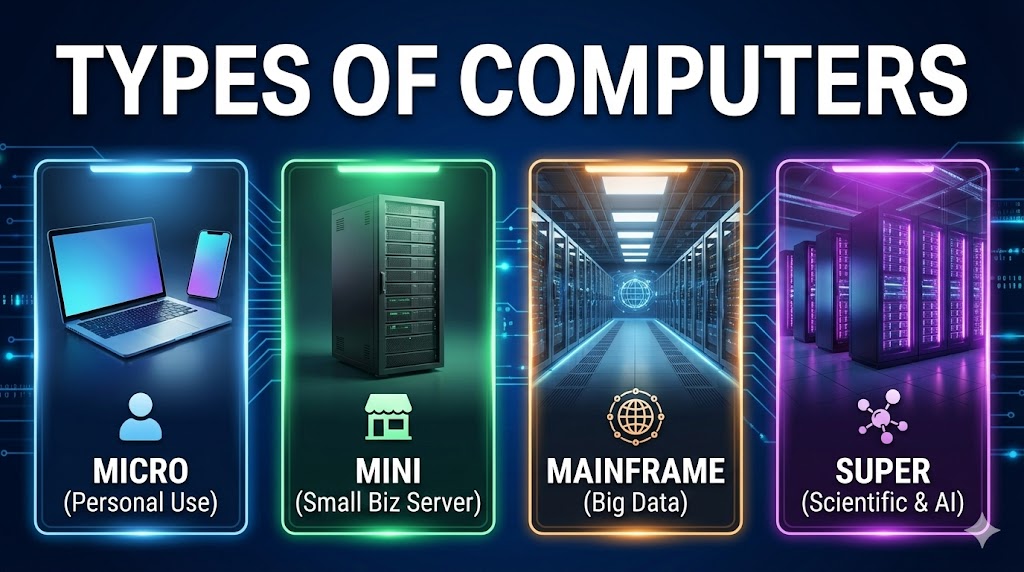
- 1. Microcomputer
This is the most common type used in homes and offices. It is affordable and designed for individual use.
Examples: Desktop PC, Laptop, Smartphone
- 2. Mini Computer
Slightly larger and faster than a microcomputer. Used by small/medium companies as servers where multiple people work together.
- 3. Mainframe Computer
Very large and expensive with huge storage. Used by large organizations like banks and railways to handle bulk data.
- 4. Supercomputer
The fastest and most powerful computer in the world, used for complex calculations.
Usage: Weather forecasting, Scientific research
Main Parts of a Computer
Just like our body has different parts to perform specific tasks, a computer is also made up of several components. All these parts work together to make the computer run.

- 1. CPU (Central Processing Unit)🗄️
This is the “Brain” of the computer. It is a box that processes all instructions and controls other parts of the computer.
- 2. Monitor 🖥️
It looks like a TV screen. It displays whatever you type or do on the computer, like movies, games, or documents.
- 3. Keyboard ⌨️
It has many buttons (keys) with letters and numbers. We use it to type information and give commands to the computer.
- 4. Mouse 🖱️
It is a pointing device. We use it to move the cursor on the screen, select items, and draw pictures.
- 5. UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply)
It keeps the computer running for a short time when the electricity goes off, allowing you to save your work.
Hardware vs. Software
Think of a computer like a human being. Hardware is like the ‘Body’ (which you can touch), and Software is like the ‘Mind’ (thoughts and instructions which you cannot touch but are necessary for the body to work).
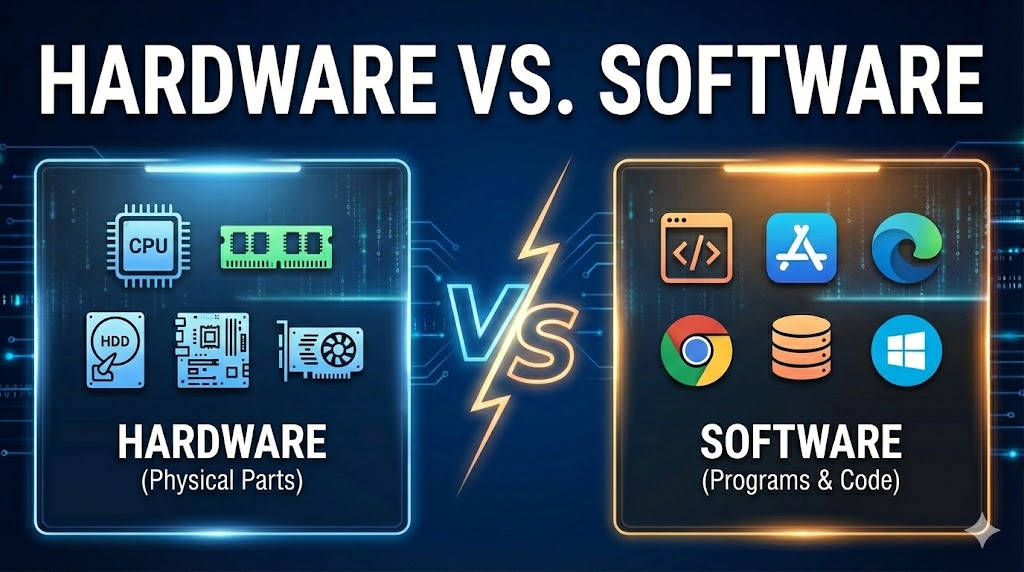
- 1. Computer Hardware
Hardware refers to the physical parts of a computer that you can see and touch. These are the machinery and electronic components. If you switch off the computer, the hardware remains there.
Examples: Monitor, CPU, Keyboard, Mouse, Hard Disk
- 2. Computer Software
Software is a set of instructions or programs that tells the hardware what to do. You cannot touch software physically; you can only see and use it on the screen.
Examples: Windows 10, MS Office, Google Chrome, Games
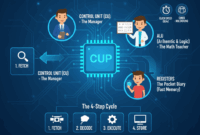
How Computer Works (IPO Cycle)
Computer works on the IPO principle. Think of a Flour Mill (Atta Chakki): You put wheat in (Input), the machine grinds it (Process), and you get flour (Output).”
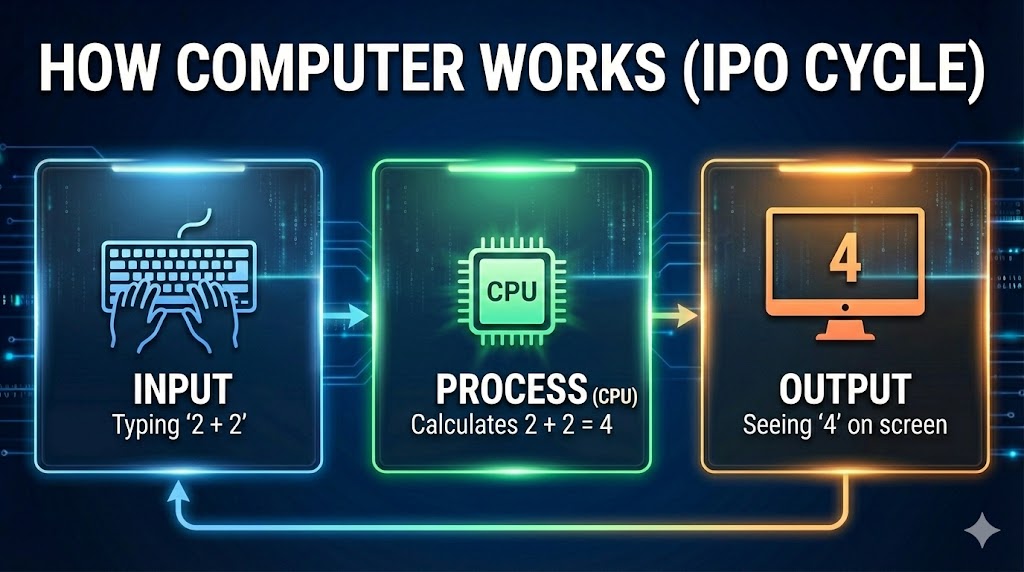
- 1. Input (Data In)
This is the first step. We give data or instructions to the computer using Input devices like a Keyboard or Mouse.
Example: Typing “2 + 2” on the keyboard.
- 2. Process (Thinking)
Once the computer receives data, the CPU starts working on it. It calculates, organizes, and solves the problem according to instructions.
Example: The CPU calculates that 2 + 2 = 4.
- 3. Output (Result Out)
Finally, the computer shows the result to the user through Output devices like a Monitor.
Example: Seeing “4” on your computer screen.
Computer Memory Units
Just like we measure weight in Kg and distance in Meters, computer data is measured in Bytes.
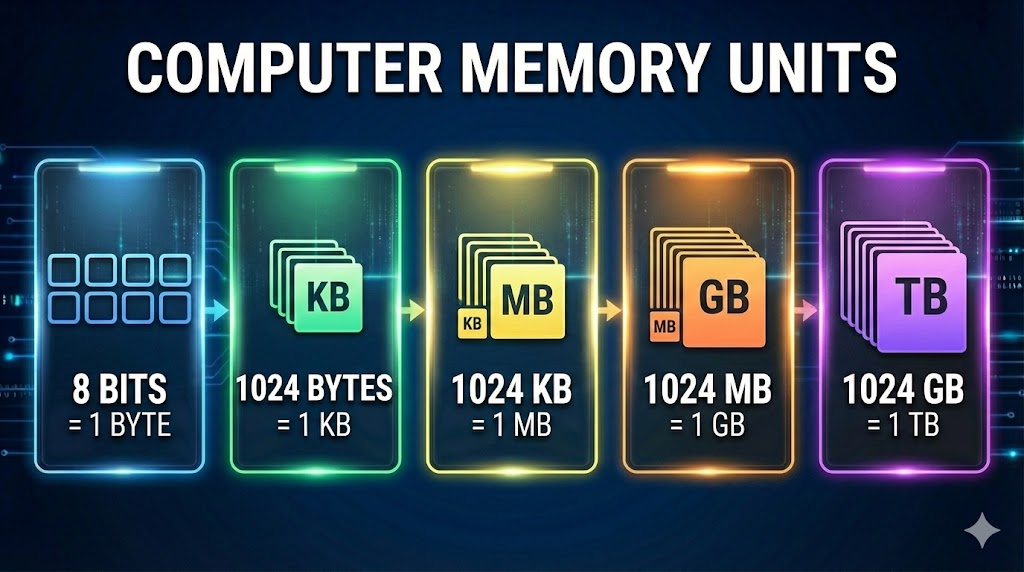
- 1. Bit & Byte (The Smallest)
Bit is the smallest unit (0 or 1). 1 Byte consists of 8 Bits. One Byte is equal to just one letter (character) typed on a screen.
Example: The letter “A” takes 1 Byte of memory.
- 2. KB (Kilobyte)
1 KB = 1024 Bytes. This is very small storage space, usually used for small text documents or tiny images.
Example: A small text note or a WhatsApp message.
- 3. MB (Megabyte)
1 MB = 1024 KB. This is the most common unit for mobile photos and songs.
Example: An MP3 song (3-5 MB) or a high-quality photo.
- 4. GB (Gigabyte)
1 GB = 1024 MB. Used for measuring movies, large games, and RAM size.
Example: An HD Movie (1-2 GB) or PUBG Mobile Game.
- 5. TB (Terabyte)
1 TB = 1024 GB. This is a huge amount of storage, usually found in computer Hard Disks.
Example: Storing 500+ Movies or 2 lakh photos.
- 8 Bits = 1 Byte
- 1024 Bytes = 1 KB (Kilobyte)
- 1024 KB = 1 MB (Megabyte)
- 1024 MB = 1 GB (Gigabyte)
- 1024 GB = 1 TB (Terabyte)
Advantages & Disadvantages
Every coin has two sides. While computers make our life easier, excessive use can cause problems too.
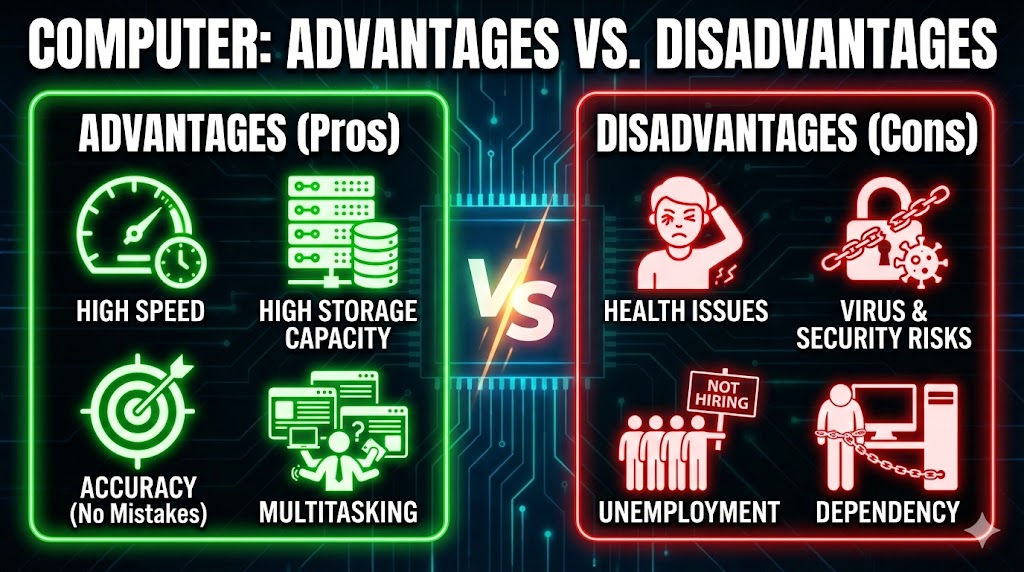
Advantages (Pros)
- 1. High Speed
Computers can perform millions of calculations in a second. A task that takes humans hours can be done in minutes.
- 2. High Storage Capacity
It can store a huge amount of data like documents, photos, and videos forever, which is impossible for the human brain.
- 3. Accuracy (No Mistakes)
Computers never make mistakes on their own. If the input is correct, the output will always be 100% accurate.
- 4. Multitasking
You can listen to music, download files, and type a document all at the same time.
Disadvantages (Cons)
- 1. Health Issues
Sitting in front of a computer for too long can cause back pain, eye strain, and headaches.
- 2. Virus & Security Risks
Computers can be infected by viruses that can steal your personal data or delete important files.
- 3. Unemployment
Since one computer can do the work of many people, it sometimes reduces the need for human workers in factories.
- 4. Dependency
We are becoming too dependent on computers. If the system crashes, all work stops completely.
Conclusion: What We Learned?
“Learning computer is like riding a bicycle. You might make mistakes in the beginning, but with practice, you will become an expert.”
- Summary
Today we covered the basics: from what a computer is, its types and parts, to how hardware and software work together.
- Practice is Key
Don’t just read about it. Try to use a computer. Create a folder, type a letter in Notepad, or draw in Paint. Practical usage is the best way to learn.
- What’s Next?
Computers are changing the world. Keep exploring new technologies like the Internet and Artificial Intelligence (AI) to stay ahead.
Have a Question?
If you have any doubts about computer basics, feel free to comment below!